Everything you need to know about Data Provenance
Data provenance is a technology field that aims to help businesses increase trust through transparency of data, specifically by tracking the origin, change, and history of data and making it verifiable.
Recently, the benefits of data provenance have become more important than ever. With the emergence of generative AI, all it takes are a few button clicks for anyone to create or manipulate data and convince others that fake data is trustworthy and real.
As digital trust erodes at an alarming rate, creators and businesses alike are looking for ways they can protect themselves from frauds and fakes, and this need to protect content has given rise to Data Provenance.
This blog post will discuss what Data Provenance is, its core use cases, and why it’s so important.
What is Data Provenance?
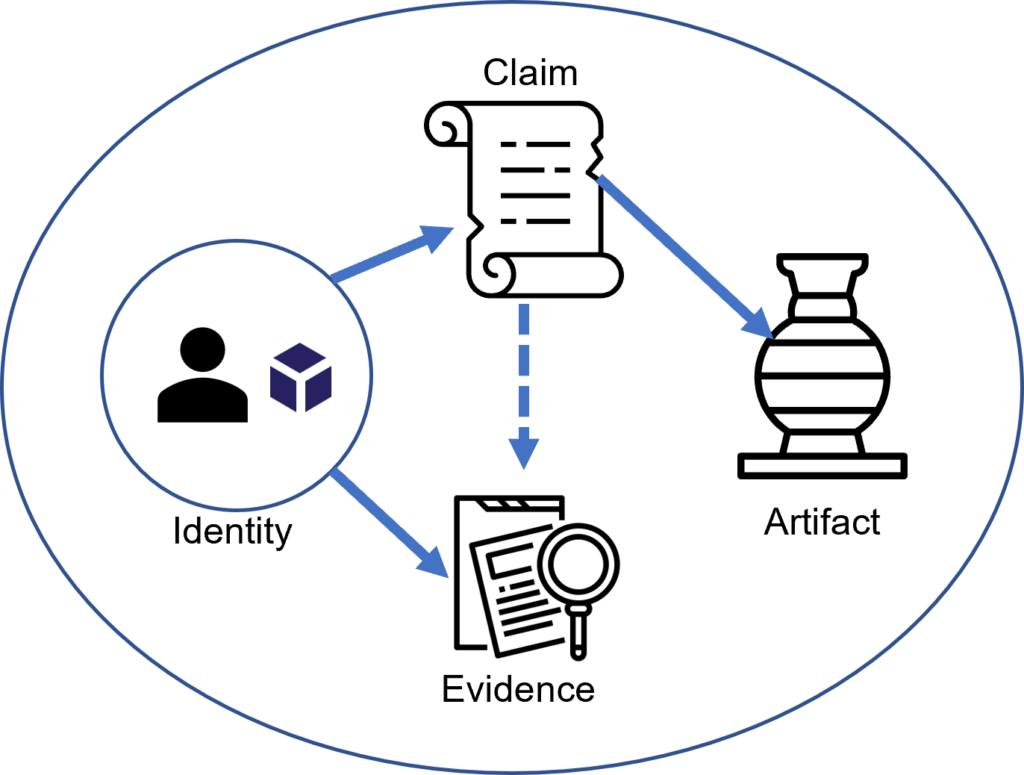
Data Provenance is the process of tracking and documenting the origin, change, and historical record of data, allowing users to understand and verify where the data came from, how it’s transformed, and by whom, to increase trust and transparency.
Businesses are increasingly dealing with risks posed by fake data. Not only could fraudulent actors try to impersonate them or modify original work, but they could find themselves ingesting and trusting false data that is used to make important decisions.
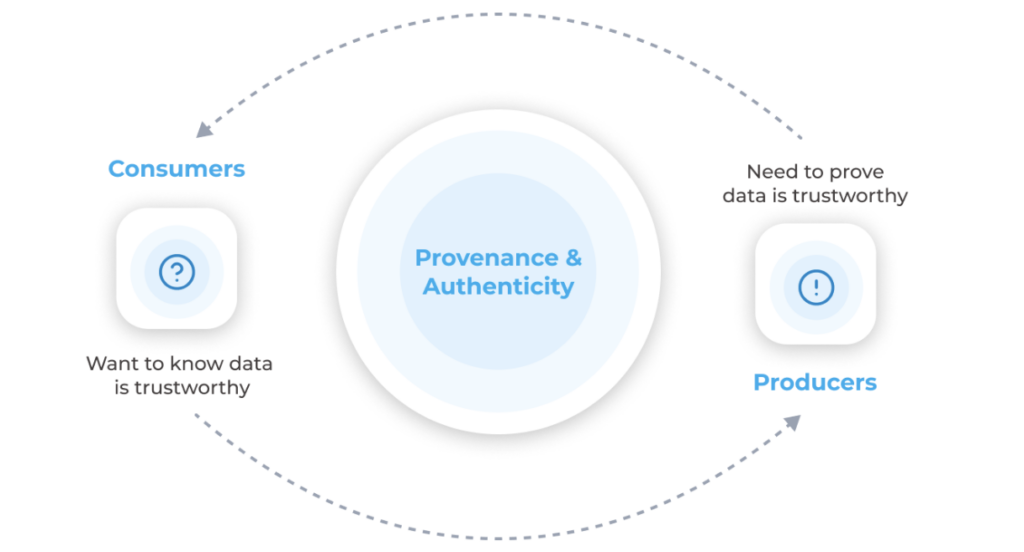
At the end of the day, people need to know if data is trustworthy. Data producers on the other hand want to prove their data is trustworthy. Data Provenance enables businesses to increase trust and transparency by showing their partners and customers where data came from and how it’s changed over time.
Applicable in a wide variety of scenarios: basically anywhere data moves around and is used in serious decision-making, strong provenance helps to streamline and automate decisions in the moment, and to verify and justify them in the future.
Common concerns such as back-dating, shredding, non-repudiation, and out-of-context use are voiced as problems in any industry working with and trusting digital documents.
How Does Data Provenance Work?
In short, Data Provenance aims to help others make informed decisions about what data or content you should confidently trust. To do this, Data Provenance platforms track metadata while making it immutable, transparent, and verifiable.
Many platforms take that information and secure it with smart contracts, hashes, blockchain, and encryption so nobody can go back and make edits without a log of all changes, thus preserving a tamper-evident record of who did what, and when throughout the lifecycle of content or data.
Data Provenance enables businesses and creators to prove ownership of content and improve trust with their users and customers. To make this a seamless experience, Data Provenance platforms automate the generation and verification of provenance metadata, and some include verification features for end-users.
Why You Need Data Provenance
Content Protection
Data Provenance ensures that content producers can prove ownership over their creations or data. Whether it’s an image, digital art, or data being produced by you or your business, data provenance can protect content from its inception and throughout its lifecycle.
Trustworthy Information
To fortify trust, Data Provenance platforms ensure data integrity by ensuring that metadata remains non-repudiable and immutable, preventing equivocation of statements and protecting evidence against unauthorized alterations or tampering during transmission or storage.
Auditable Trails
Data authenticity is confirmed by enabling auditable trails of data origin and its evolution, guaranteeing that data genuinely comes from the declared source and is the correct and latest version published.
Standards Groups Working On Data Provenance
There exist several organizations, consortiums, and businesses working to improve the capabilities and ease of access to Data Provenance.
Standards Bodies
- SCITT: Supply Chain Integrity, Transparency, and Trust (SCITT) is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) chartered working group. Its goal is to propose standards around how to continuously verify the authenticity of goods and services and ensure that when others interact with or change data, there is an immutable and auditable record.
- C2PA: The Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity is a standards body working to address misleading information online through a technical standard that certifies the source and history of media content. Essentially, C2PA is working to establish a common language that can communicate Data Provenance.
Consortia
- CAI: The Content Authenticity Initiative is an Adobe-led community of media, tech companies, NGOs, academics, and other creators working to promote and integrate the C2PA standard into their workflows, tools, and practices. CAI’s mission is to increase trust and transparency online with an industry-wide attribution framework that empowers creatives and consumers alike.
- Partnership on AI: The Partnership on AI is a community that includes members from academic, civil society, industry, and media aiming to produce positive outcomes from AI development, including synthetic media transparency, AI and media integrity, and responsible deployment and research of algorithmic systems.
Data Provenance Use Cases
Businesses Ensuring Data Authenticity:
- Proof of Originality: Provenance can help content businesses prove that they were the original creators of a piece of content, be it data, an article, artwork, music, or video.
- Content Authenticity: Content has a broad definition, meaning any file or data. Provenance can help verify the authenticity of sources and information, ensuring that the content is reliable and trustworthy.
- Data Misuse: Importantly, businesses need to know how data within their organization is being used. What’s being uploaded, by whom, and when are important factors to consider when reviewing how employees are using your cloud storage. On the other hand, businesses need ways to prove what’s wrong or right when it comes to others making claims over their data.
Responsible AI:
- Algorithmic Transparency: Data provenance is crucial for tracing the datasets used in training AI models. This helps in understanding the decisions made by AI, ensuring transparency in how models arrive at conclusions.
- Bias Detection and Mitigation: By tracking the origins and composition of training data, provenance can help identify potential biases in datasets, allowing for corrective measures to be taken.
- Compliance and Ethical Standards: In sectors where AI decisions have significant impacts (like healthcare or finance), provenance ensures that AI models comply with ethical standards and regulatory requirements.
- Model Evolution Tracking: As AI models evolve over time with new data and retraining, provenance provides a history of these changes, helping to understand and justify the evolution of the model’s decision-making process.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance):
- Traceability of Claims: Companies often make claims about their environmental and social practices. Provenance can help verify these claims by tracing the source and validation of the data.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: For companies committed to sustainable sourcing, provenance can trace the origins of materials to ensure they are sustainably sourced.
- Transparency and Reporting: Stakeholders, including investors and consumers, demand transparency in ESG practices. Data provenance can provide a verifiable trail of ESG data, ensuring that companies are accountable for their claims.
Supply Chains:
- Product Authenticity: Provenance can help verify the authenticity of products, ensuring that they are not counterfeit.
- Ethical Sourcing: Companies can trace the origins of their products to ensure they are sourced ethically, without child labor or in violation of other ethical standards.
- Recall Efficiency: If a product defect is discovered, provenance can help identify the source of the defect and which products are affected, making recalls more efficient.
- Regulatory Compliance: For industries with strict regulations on sourcing and product ingredients (like food or pharmaceuticals), provenance can help ensure compliance by tracing the origins and processing of all components.
Software Development and Maintenance:
- Code Authenticity: Provenance can help verify the origins of code, ensuring that it hasn’t been tampered with or that it doesn’t contain malicious components. Software Bills of Materials (SBOMs) are increasingly popular and need provenance as they are used to verify the authenticity and validity of software and code.
- License Compliance: Software often uses libraries or components with specific licenses. Provenance can help track the origins and licenses of all components, ensuring compliance and avoiding legal issues.
- Version Control: While version control systems like Git inherently provide some level of provenance, further provenance tools can offer additional layers of traceability, especially in complex software ecosystems.
- Bug Tracking and Resolution: By understanding the history and changes made to a piece of software, developers can more easily identify when and how a bug was introduced, aiding in its resolution.
Invoices and Contracts:
- Audit Trails for Transactions: Provenance can provide a detailed history of the creation, modification, and execution of contracts, aiding in audits and legal verifications.
- Fraud Detection: By tracking the origins and changes in contracts and invoices, provenance can help detect anomalies or fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized alterations.
- Compliance Verification: In industries with strict regulatory requirements, provenance ensures that all contractual agreements and invoicing practices comply with legal standards.
- Dispute Resolution: In cases of disputes, the historical data provided by provenance can be invaluable in resolving conflicts over contract terms or invoicing details.
Build vs. Buy
Building a Data Provenance platform is quite difficult. Not only does it require a team of engineers, but building a platform can take months to years depending on their experience.
Some of the underlying technology in Data Provenance platforms includes:
- Blockchain and distributed ledgers
- Smart contracts
- Encryption
- Verifiable receipts
- Blob storage
- Merkle trees
- Identity verification
Figuring out how to put all those technologies together is very difficult. And you’d be paying for both the technology needed to build the platform and the wages of engineers for months to years trying to build such a platform.
Importantly, there’s no competitive advantage to building your own Data Provenance platform. While the benefits of Data Provenance are far-reaching, having your own platform offers no edge over the competition. Your provenance and another’s provenance are the same.
Think of it like this: do you need your own search engine for your business or is using Google good enough?
Summary
Data Provenance solves the problem of trustworthy content and data. If you want to ensure that you, your business, or your customers are protected from generative AI and can make decisions with confidence, then Data Provenance is the solution for you.
If you’d like to get started with a fully managed Data Provenance platform, sign up for a DataTrails free trial today or get in touch with us here.